Driving safely is a shared responsibility, and understanding the factors that contribute to road safety is crucial for everyone. The Idaho Transportation Department’s Office of Highway Safety (OHS) plays a vital role in collecting, analyzing, and disseminating information related to traffic crashes and safety initiatives across the state. This information is publicly accessible and designed to help make Idaho’s roads safer for all users.
This article delves into the resources and information provided by the OHS, covering everything from accessing crash records and statistical data to child passenger safety and grant programs. Whether you are a concerned citizen, a researcher, or a safety advocate, the data and programs outlined here are invaluable for promoting safer driving habits and reducing accidents. Understanding these resources is the first step towards contributing to a safer driving environment for yourself, your family, and your community.
Accessing Idaho Crash Records and Data
Crash records are public information and available to anyone who needs them. The OHS, in accordance with Idaho Code, provides access to these records, with a nominal fee to cover costs.
You can easily request crash reports online through the ITD Forms – Crash Reports portal. For a fee of $7.00 plus a transaction charge, you can obtain a copy of a specific crash report. Beyond individual reports, the OHS also offers statistical information not found in the annual Idaho Traffic Crash Reports. For detailed statistical inquiries, additional charges may apply depending on the complexity and scope of the request.
For specific questions about Idaho’s crash reporting systems, including eImpact, WebCARS, or the SWET (State-Wide Electronic Ticketing) application, you can reach out via email to [email protected].
The Importance of Crash Data Analysis
Each year, thousands of crashes occur on Idaho roads. The systematic collection and analysis of crash reports are essential functions of the OHS. This data-driven approach allows the OHS to make informed decisions that improve Idaho’s transportation system and protect those who use it. By understanding the factors that contribute to crashes, the OHS can develop targeted safety programs and allocate resources effectively.
A Vehicle Crash Report (VCR) is mandatory for every crash meeting specific criteria: involvement of a motor vehicle, occurrence on public property, and resulting in property damage exceeding $1500 to any single involved party, or any injury to anyone involved. Law enforcement officers at the scene meticulously document various contributing factors, covering environmental conditions (location, road conditions), vehicle details, and person-related information.
Once completed, the law enforcement agency electronically submits the crash report to the OHS. Here, a trained crash analyst reviews each report for accuracy before entering the data into Idaho’s comprehensive crash database. This rigorous process ensures data integrity and reliability for analysis and decision-making.
Public Access to Crash Data
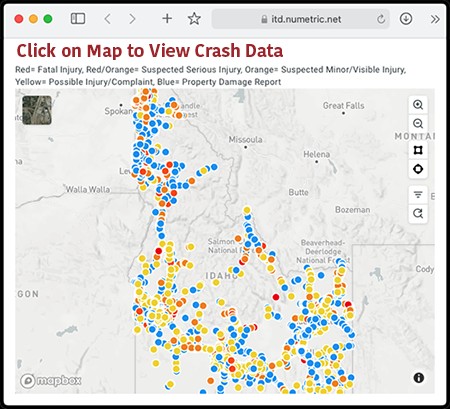
Promoting public awareness and informed decision-making is a priority for the OHS. To this end, they make crash data publicly accessible online and in printed reports. The Crash Map is a valuable online tool for visualizing and exploring crash data.
To help users navigate this data, the OHS provides a Training Video for the Crash Data Dashboards. This video tutorial guides users on how to effectively use the ITD Crash Data Dashboards to explore crash trends and data through dynamic charts, graphs, and maps. The dashboard’s interactive nature allows users to apply custom filters for targeted data searches.
ITD Crash Data Dashboards
The ITD Crash Data Dashboards are a powerful resource for anyone seeking to understand crash trends in Idaho. These dashboards feature dynamic charts, graphs, and maps that visualize crash data. Users can apply filters to customize searches and analyze specific aspects of crash data relevant to their interests.
In addition to the online dashboards, the OHS publishes the annual Traffic Crash Report for Idaho. This comprehensive report provides a detailed tabulation, analysis, and summary of various aspects of traffic collisions in the state. The report is thoughtfully organized into sections to facilitate easy access to specific information.
Accessing Annual Traffic Crash Reports
The OHS provides easily accessible annual Traffic Crash Reports, offering detailed insights into traffic safety trends over the years. These reports are available for download in PDF format, providing comprehensive data and analysis.
2023 Traffic Crash Report
Idaho Traffic Crashes 2023 (Full report PDF)
Fatality Information by ITD District 2019-2023 (Excel file)
Collision Report by Sections (Links to specific sections would be listed here in the original article)
2022 Traffic Crash Report
Idaho Traffic Crashes 2022 (Full report PDF)
Fatality Information by ITD District 2018-2022 (Excel file)
Collision Report by Sections (Links to specific sections would be listed here in the original article)
2021 Traffic Crash Report
Idaho Traffic Crashes 2021 (Full report PDF)
Fatality Information by ITD District 2017-2021 (Excel file)
Collision Report by Sections (Links to specific sections would be listed here in the original article)
2020 Traffic Crash Report
Idaho Traffic Crashes 2020 (Full report PDF)
Fatality Information by ITD District 2015-2019 (Excel file)
Collision Report by Sections (Links to specific sections would be listed here in the original article)
2019 Traffic Crash Report
Idaho Traffic Crashes 2019 (Full report PDF)
Fatality Information by ITD District 2015-2019 (Excel file)
Collision Report by Sections (Links to specific sections would be listed here in the original article)
Child Passenger Safety: Protecting Idaho’s Youngest Travelers
Child passenger safety is a paramount concern, and the OHS is dedicated to providing resources and guidance to ensure children are safely transported in vehicles. Carma McKinnon serves as the statewide Child Passenger Safety Centralized Leadership coordinator and is a valuable resource for any questions or assistance related to child passenger safety. You can contact Carma at 208-742-1683 or [email protected].
Child Restraint Recommendations by Age and Size
Choosing the right car seat and using it correctly is vital for protecting children in vehicles. The OHS provides clear recommendations based on a child’s age and size:
Rear Facing Seat:
- For children up to 2 years of age, or until they reach the car seat manufacturer’s highest weight and height limits.
Forward Facing Seat:
- For children up to the car seat’s upper height and weight limits, approximately 4 years old and between 40-65 pounds.
- The top tether should be used for forward-facing seats until the child weighs 40 pounds.
Booster Seat:
- For children approximately 4 to at least 8 years old or under 4’9” tall.
- Use a high-back or backless belt-positioning booster seat.
- Lap-belt-only seating positions are not suitable for booster seats.
Adult Seat Belt:
- For children age 8 or older and at least 4’9” tall.
- The lap belt should lie across the upper thighs, and the shoulder belt across the chest. Knees should bend comfortably at the seat edge.
For more detailed guidance on choosing the right car seat, refer to the Car Seat Recommendations: Choosing the Right Seat resource from safercar.gov.
Child Restraint Basics Pocket Card
The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) has developed a helpful Child Restraint Basics – Pocket Card. This free resource provides concise recommendations for parents and caregivers on selecting and using child restraints based on a child’s height, weight, and age.
To request a pocket card by mail, contact Lisa Losness, Child Passenger Safety Program, ITD Office of Highway Safety at 208-334-8103 or [email protected].
Seguridad para el Niño Pasajero (Child Passenger Safety in Spanish)
The OHS also provides resources in Spanish to ensure child passenger safety information is accessible to a wider audience. For information on distribution points for safety materials or to obtain a WHALE Kit (discussed later), contact Lisa Losness at the contact information provided above.
Four Key Child Safety Steps
The OHS emphasizes four crucial steps for child passenger safety:
- Restrain children on every trip, every time.
- Keep children in the back seat until age 13.
- Use the correct safety seat for the child’s size.
- Use child safety seats and seat belts correctly.
Important Details for Your Child’s Safety Seat
Child Safety Seat Ratings: NHTSA’s ease-of-use rating program helps parents and caregivers understand the features of different child safety seats and identify those that are user-friendly.
Car Seat Registration: Registering your car seat is essential. It allows the manufacturer to contact you in case of recalls or safety notices, ensuring your child’s seat meets all Federal Safety Standards.
Used Child Safety Seats: The OHS strongly advises against buying or selling used car seats. Car seats have an expiration date, typically six years from the manufacture date, due to material degradation over time. For guidance on disposing of a used car seat, refer to Consumer Reports’ information on retiring car seats.
Child Safety Seat Check Sites
Ensuring proper car seat installation is critical. The OHS provides a resource to find Car Seat Inspection sites in your area. Trained professionals at these sites can check your car seat installation and provide guidance.
• Click here to find locations for Car Seat Inspection sites in your area.
If no local sites are available, contact Carma McKinnon for assistance. Always thoroughly read and understand the installation and usage instructions for your specific car seat and booster seat. Regular checks by certified technicians significantly enhance a child’s safety in a crash.
Become a Car Seat Technician
To further enhance child passenger safety in Idaho, the OHS encourages individuals to Become a Car Seat Technician. National surveys by NHTSA indicate that over 80% of car seats are installed incorrectly. Certified Child Passenger Safety Technicians play a crucial role in educating parents and caregivers on proper car seat installation.
The NHTSA Standardized Child Passenger Safety Training course provides comprehensive knowledge and skills for certification as a Child Passenger Safety Technician. This 3-4 day course includes hands-on skills checks and knowledge assessments. While rewarding, the course is physically demanding, requiring participants to climb in and out of vehicles and apply pressure to install car seats correctly. Online registration is available through the National SAFE KIDS website, with a registration fee of $95.00 that covers the course manual and a 2-year NHTSA National Child Passenger Safety Certification. Recertification is required every two years to maintain certification.
For course availability in Idaho or further questions, contact Carma McKinnon.
The WHALE Program – “We Have A Little Emergency”
The WHALE program (We Have A Little Emergency) is an invaluable tool for emergency responders in Idaho. It helps them quickly identify young children involved in car crashes, especially when adult occupants are unable to communicate.
The WHALE Kit includes an identification card to attach to the car seat, containing the child’s name, photo, medical information, and emergency contact details. WHALE stickers are also included for car windows and the safety seat to alert emergency personnel. This simple system can provide crucial information to first responders, helping them comfort and care for child patients effectively.
- WHALE brochure in English
- WHALE brochure in Spanish
WHALE Kits are available in both English and Spanish. For information on obtaining a WHALE Kit or distribution points, contact Lisa Losness.
Car Seat Law and Useful Links
Idaho’s Child Restraint Law: Idaho law mandates that all children 6 years of age or younger must be properly restrained in an appropriate child safety restraint. This primary law carries penalties for infractions, detailed on the Idaho Supreme Court’s website Infraction Penalty Schedule.
Child Passenger Safety Laws in Other States: For those traveling outside Idaho, it’s important to be aware that child passenger safety laws vary by state. A resource for other states’ laws is available through the Governors Highway Safety Association (GHSA).
Partners for Child Passenger Safety: (Information about partnerships would be included here if available in the original article)
Contact Lisa Losness for more information on child passenger safety programs and resources.
Addressing Aggressive Driving
Aggressive driving is a dangerous behavior contributing significantly to traffic incidents. It stems from frustration and a disregard for other motorists’ safety. Many aggressive drivers underestimate the risks, believing a ticket is the worst consequence, but aggressive driving can have fatal outcomes.
For more information on aggressive driving, visit shift-idaho.org/aggressive-driving.
Characteristics of Aggressive Drivers:
- Ignoring traffic signals
- Speeding and tailgating
- Driving too fast for conditions
- Weaving in and out of traffic
- Improper and abrupt lane changes
- Passing on the shoulder
- Hand and facial gestures
- Screaming, honking, and flashing lights
Responding to Aggressive Drivers:
- Safely move out of their way.
- Remain calm; your safety is the priority.
- Do not challenge them.
- Avoid eye contact.
- Ignore and do not reciprocate gestures.
- Report aggressive driving incidents (vehicle description, license number, location).
- Always wear your seat belt.
Reporting Aggressive Drivers:
- Find a safe location to call 911.
- Be ready to provide location, vehicle description, and license plate details.
- Report an Aggressive Driver using the provided resource.
Road Rage: Road rage is a criminal act defined as deliberate violence towards another driver. It is a serious and increasingly common offense.
For information about Aggressive Driving education and safety awareness in Idaho, contact Josephine Middleton.
Combating Distracted Driving
Distracted driving, as defined by NHTSA, is a form of inattention where drivers divert their focus from driving to other activities. Distractions can be electronic (cell phones, navigation systems) or conventional (passengers, eating). Distractions fall into three categories:
- Visual – taking eyes off the road.
- Manual – taking hands off the wheel.
- Cognitive – taking mind off driving.
For more information, visit shift-idaho.org.
Research highlights the alarming prevalence of distracted driving. A Virginia Tech Transportation Institute (VTTI) study in 2006 found that driver inattention was a factor in nearly 80% of crashes and 65% of near-crashes within three seconds before the event. Activities like reaching for moving objects (9 times greater risk) and drowsiness (4 times greater risk) significantly increased crash risk. Cell phone use and other electronic device usage are major and growing concerns.
Distracted Driving is a key focus area in the Idaho Transportation Department’s Strategic Highway Safety Plan.
Distracted Driving Prevention Resources and Policies: (Links to resources and policy samples would be included here if available in the original article)
Toolkit: The Distracted Driving Task Force provides a toolkit of materials to raise awareness about the dangers of distracted driving.
Crash Information and Statistics
TEMPLATES: (Links to templates for Employer Policies, Newsletters, Presentations, Press Releases would be included here if available in the original article)
The Importance of Seat Belts
Seat belts are a fundamental safety feature, and consistent seat belt use is crucial for driver and passenger safety.
Buckle Up, Idaho Campaign & SHIFT | Drive Well Idaho
The OHS promotes seat belt use through campaigns like “Buckle Up, Idaho” and the broader SHIFT | Drive Well Idaho initiative, which encourages engaged driving. Learn more at shift-idaho.org.
Join the Conversation: Watch the VIDEO: Driving in the Moment to reinforce safe driving practices.
Seat Belt Surveys & Idaho’s Seat Belt Law
The OHS conducts annual observational seat belt surveys across 100 sites in Idaho to estimate seat belt usage rates statewide.
Idaho’s Seat Belt Law: Idaho Code 49-673 mandates seat belt use for everyone in a vehicle. Key provisions include:
- $10 citation for adult (18+) violators.
- Adult drivers are ticketed for unrestrained passengers under 18.
- Drivers under 18 and any unrestrained occupants under 18 face fines and court costs.
- Law enforcement can issue citations solely for seat belt violations, but a primary traffic stop must occur for another violation.
For current infraction penalties and fees, consult the Idaho Supreme Court’s Infraction Penalty Schedule.
Youth Education and Teen Driving Safety
The OHS provides free educational materials to qualified organizations for public distribution, particularly targeting youth education and teen driving safety.
Young Driver Education:
Distracted driving is a major factor in serious and fatal crashes, especially among young drivers. Avoiding distractions like texting, cell phone use, eating, or drinking while driving is crucial.
Resource: The OHS encourages youth involvement in promoting safe driving. Share initiatives from your school or community about distracted driving prevention by sending links or information to [email protected].
Grant Programs & Funding for Highway Safety Initiatives
The ITD Office of Highway Safety (OHS) provides grant funding to support initiatives addressing critical behavior-related traffic safety areas, including impaired driving, aggressive driving, distracted driving, occupant protection, bicycle, pedestrian, motorcycle safety, youthful drivers, and traffic records. These grants aim to address traffic safety deficiencies, expand effective programs, and develop new safety interventions.
While specific details about past programs like a 2018 Aaa Car Seat Grant Donation Program are not detailed in this document, the OHS actively supports various grant opportunities to enhance child passenger safety and broader highway safety across Idaho. These grants may support initiatives such as car seat donation programs, educational campaigns, and enhanced enforcement efforts. Organizations interested in pursuing funding for traffic safety projects are encouraged to explore current grant opportunities through the OHS.
Grant Opportunities:
FY26 Grants: Oct. 1, 2025 – Sept. 30, 2026: Note that the application period for year-long FY26 grants has closed.
FY25 Traffic Enforcement Grant Project Agreement: This includes Mini Grants and Mobilization Requests. Agencies can participate in FY25 High Visibility Enforcement mobilizations and apply for mini-grant funding and E-citation equipment by submitting the required documents. For inquiries, contact [email protected] or 208-334-4460.
Highway Safety Plans & Annual Reports
To secure federal highway safety funding, each state must submit a High Safety Plan. This plan outlines the state’s process for identifying highway safety problems, defining performance measures, setting safety goals, and developing projects to address these issues. The plan, approved by the Governor’s Representative for Highway Safety, details planned projects, countermeasure strategies, and their link to the state’s safety goals.
States are also required to submit an Annual Report within 90 days of the federal fiscal year’s end. This report evaluates progress towards highway safety goals, using performance measures from the High Safety Plan, and describes how funded projects contributed to achieving these goals.
Traffic Safety Problem Identification
Identifying traffic safety problems involves analyzing collision data to pinpoint subgroups of drivers, pedestrians, vehicles, or roadways with statistically higher collision rates than expected. This analysis considers factors like population, licensed drivers, registered vehicles, vehicle miles traveled, and characteristics of specific subgroups.
Idaho’s problem identification process begins by evaluating the state’s experience in NHTSA’s eight highway safety priority areas. Other potential problem areas are identified through Idaho collision data analysis, suggestions from the Idaho Traffic Safety Commission (ITSC) and OHS staff, and research into issues identified by other states. All identified traffic safety problems are validated with data and require effective countermeasures eligible for federal highway safety funds.
Current traffic safety problem areas being addressed include: Aggressive Driving, Occupant Protection, Impaired Driving, Distracted Driving, Youthful Drivers, Pedestrian Safety, Bicycle Safety, Motorcycle Safety, Traffic Records, and Emergency Medical Services.
Forms & Resources
Ignition Interlock Providers
An ignition interlock device measures breath alcohol concentration (BAC) and prevents vehicle startup if BAC exceeds .025. Idaho requires certified providers for these devices.
The Ignition Interlock Providers List lists ITD-certified manufacturers meeting NHTSA standards. Individuals required to install an ignition interlock must contact listed companies directly to arrange service. The ITD does not install ignition interlocks and cannot recommend specific providers. Contact ITD Driver Services at 208-334-8000 for ignition interlock questions.
Coroner Forms & Highway Safety Web Links
Coroner Forms:
- Coroner’s Report of Motor Vehicle Crash Fatality Form (Word Document)
- HIPAA – NHTSA designated as a “Public Health Authority (PDF)
- Idaho Statutes concerning reporting of deaths and testing of blood (PDF)
Highway Safety Web Links:
Contacts: Office of Highway Safety (OHS)
Who We Are
Responsibilities: The Office of Highway Safety is responsible for maintaining the Statewide Collision Database, analyzing crash statistics, and administering federal section 402 highway safety funds.
Location: The OHS is located at the Idaho Transportation Department (ITD) headquarters complex in Boise, in the East Annex building: 3293 W. Jordan Street, Boise, Idaho 83703.
Mailing Address: Idaho Transportation Department-Office of Highway Safety | PO Box 7129 Boise, ID 83707-1129.
Phone: 208-334-8100 | Fax: 208-334-4430.
Organizational Structure: The OHS is part of the Division of Engineering Products and Plans (DEPP) within the ITD. It collaborates with other ITD sections and districts to enhance road safety. The ITD Director is the Governor’s highway safety representative. The OHS is managed by the Highway Safety Manager and includes Records and Programs teams. Funding decisions are subject to approval by the Idaho Traffic Safety Commission and the Idaho Transportation Board.
Office of Highway Safety Staff
Contact the Highway Safety section at 208-334-8000 or FAX 208-334-4430, or contact specific staff members directly (staff contact information would be listed here in the original article).
Mission, Vision, and Operating Philosophy
Mission Statement: To support the Department’s mission of ”Your Safety. Your Mobility. Your Economic Opportunity” by implementing programs to eliminate traffic deaths, serious injuries, and economic losses. This is achieved through funding safety programs, promoting safe travel, and utilizing reliable crash data.
Vision Statement: To be a national leader in promoting road safety in Idaho efficiently and effectively.
Operating Philosophy: The OHS prioritizes public welfare and saving lives through innovative and effective highway safety programs across all transportation modes. They are committed to their role in ensuring safe travel in Idaho and strive to make a positive impact. Partnerships are essential to their success. The OHS focuses on identifying traffic safety trends, providing accurate data for decision-making, developing impactful safety programs, and allocating safety funds to address local traffic safety issues. Teamwork, integrity, and a positive work environment are core values. They are committed to being leaders in a coordinated statewide effort to eliminate traffic fatalities and serious injuries in Idaho.
For comments, questions, and suggestions, email [email protected] or write to: Idaho Transportation Department – Office of Highway Safety P.O. Box 7129 Boise, Idaho 83707-1129.